Eduardo Chillida, the Basque artist, put in considered one of his best-known collection of sculptures on the breakwater of Donostia and referred to as it “The Comb of the Wind.” And there’s something of that within the wind generators which might be starting to populate the coastal waters of many nations. Between 2020 and 2021, the power capability of those “wind combs” will nearly double, reaching 48.2 GW. In flip, floating offshore wind has begun to symbolize a major a part of the entire put in wind farm on a world scale.
On this article, you’ll find the next contents:
What’s floating offshore wind, and the way does it work?
The standard method to putting in offshore wind farms has been to maneuver onshore wind turbine structures to shallow coastal waters. One of many causes is that offshore winds are extra steady and intense, as they don’t face obstacles as onshore, similar to mountains or forested areas.
One of many challenges of offshore wind energy is to repair the constructions of those wind generators to the seabed and make them sturdy sufficient to resist the onslaught of waves. The truth that it’s obligatory to put in such a assist limits its potentialities to the continental shelf closest to land in shallow waters.
Floating platforms, often known as Floating Offshore Wind Platforms (FOWP), overcome a few of these pitfalls by utilizing floating constructions related to the platform by metal or different cables. These cables preserve the platform stationary whereas offering some mobility in very sturdy waves.

Benefits of floating offshore wind generators
As could be seen, the floating offshore wind power method gives quite a few benefits, together with the next:
- It may be put in in deep waters
- Might be simply moved in case of want
- Diminished environmental impact on the seabed
- Decrease set up price
- It harnesses stronger winds
- Diminished visible impression by having the ability to be put in at a higher distance from the shoreline
Kinds of floating offshore wind
To a big extent, the wind generators used on the platforms are likely to share comparable traits, aside from some developments that use two-bladed windmills. The primary distinction is underwater, in the kind of floating platforms used. On this regard, the next variants could possibly be talked about:
- Spar buoy. This platform makes use of a cylindrical base that gives a easy and environment friendly design, with the burden utilized on the decrease finish. It requires multiple hundred meters of depth to function correctly.
- Barge or pontoon mannequin. Not like the Spar design, the platform is extra like a ship when it comes to size and width.
- Semi-submersible base. It makes use of a number of semi-submersible cylinders related using beams.
- TLP mannequin (Pressure Leg Platform). It’s primarily based on a central column and arms related to the tensioners to make sure stability.
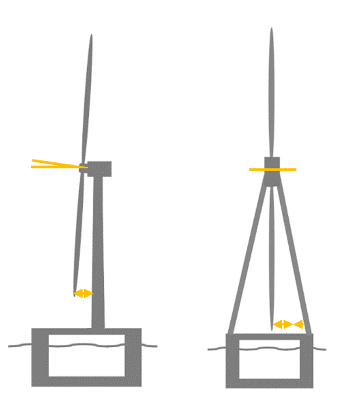
Wind pyramids: an modern method
One of many few fashions through which probably the most marked divergences are manifested on the floor is the proposal of the French firm Eolink. It is because the wind turbine is conceived from the outset as a mannequin meant for floating offshore wind, and its whole design leverages the particularities of the setting.
On land, wind generators use a design referred to as a “nacelle.” That’s, with an ovoid physique like aircraft engines. This design permits a heavy construction to behave like a head that turns and “faces” the course of the wind. Mobility at sea, alternatively, may be very completely different. And that’s the first differentiating issue of the “pyramidal” generators.
The mannequin proposed by Eolink dispenses with the nacelle and is inserted right into a pyramidal construction composed of 4 masts. Right here it’s the whole platform that rotates, as an alternative of the wind turbine head. A nacelle turbine has weight limitations and much more so at sea, the place waves and robust winds expose it to loads of put on and tear. Consider a really heavy “head” with a skinny neck to know this. However, the mixed mast construction can maintain a lot bigger generators.
One other method to cut back put on and tear on the construction of a wind turbine is to use versatile blades. The issue with the nacelle mannequin is that the proximity of the principle mast prevents the usage of blades which might be too lengthy and versatile, as they may impression it.
In line with its builders, the “pyramid” of masts reduces the chance of impression and permits the usage of longer and extra versatile blades, leading to higher energy efficiency. As well as, this construction distributes weight higher and improves power.
Coupled with a brand new floating platform design with a buoy at a depth of 20 meters, the brand new wind generators might produce 20 MW per unit with an effectivity 20-25 % increased than present reference options.
This modern floating offshore wind method remains to be within the prototype section, however the producer plans to put in an indication wind turbine with a capability of 5 MW within the close to future.
Sources











