UX metrics assist determine the place customers battle when utilizing an app or web site and the place they’re profitable. The info collected helps designers, builders, and product managers make enhancements to ship an optimized consumer expertise.
In the event you’re new to UX metrics, these are those to deal with first.
Process Success Price
Process success charge (TSR) is the share of duties a consumer efficiently completes after they’re in your web site. A excessive quantity suggests customers use your web site with minimal friction. A decrease quantity means your design and performance needs to be tweaked to make issues smoother.
Process success charge is measured with two items of information–an outlined objective and a definition of success. You calculate job success charge by dividing the variety of duties the consumer accomplished efficiently by the variety of complete duties tried. The formulation seems like this:
Process success charge = (# of efficiently accomplished duties / complete # of tried duties) x 100
Anybody working an ecommerce web site loves this UX metric. It helps UX groups optimize the sale course of for customers. It is usually simple to measure.
Let’s say the objective is to finish a sale. You already know you hit that objective when the checkout affirmation display screen shows.
If 1,000 customers make it to the checkout web page (makes an attempt) and 600 make it to the affirmation web page (success), the duty success charge is 60%. This isn’t a very spectacular TSR. Research have proven that around 78% is the average task completion rate.
This helps the UX group zero in on particular areas for enchancment. They will streamline their strategy and allocate sources successfully. This avoids reinventing the wheel when only a spoke is damaged. Process error charge helps UX groups discover the damaged spoke.
Time on Process
Time on job (TOT) tells you ways lengthy it takes a consumer to finish a job. This metric is straight associated to how simple and user-friendly an expertise is. The quicker a consumer can end one thing, the extra glad they typically are. Conversely, in the event that they battle to perform the duty, the extra possible they’re to bounce.
Calculating TOT requires you to find out the objective, then observe a consumer from a place to begin to an ending level of that objective. The time in between the 2 values is the time on job.
Time on Process = Finish Time – Begin Time
Time on job isn’t a one-size-fits-all quantity, and it’s not at all times about pace. Completely different duties take totally different quantities of time, particularly for brand new customers versus skilled ones. There may be even a case to be made {that a} longer time on job can capture user engagement and interest.
Measuring a single consumer’s TOT isn’t useful. The true worth comes when the information will be aggregated to find out common job occasions for various consumer teams and particular duties. To extract the actual worth from this metric, begin by benchmarking TOT for particular consumer teams, then examine TOT over time.
This combination information, mixed with different metrics like error charge and job success charge, helps UX groups pinpoint the precise duties that could be inflicting customers complications. The group can then redesign course of flows, create a extra streamlined expertise, and cut back time on job for core processes. This results in elevated buyer satisfaction.
Error Price
Error charge exhibits what number of occasions a product consumer makes a mistake whereas utilizing an internet site or app. This consists of issues like opening the improper web page, mistyping data right into a type subject, or clicking an space that isn’t clickable. Understanding error charges helps determine ache factors within the consumer expertise.
Why is that this essential? Jakob’s Law states that customers need your web site to perform like the opposite websites they repeatedly use. When your web site diverges from these expectations, customers make errors and error charges go up.
To calculate error charge for a job, you have to know the variety of errors and the overall variety of job makes an attempt.
Error Price = (# of errors / complete variety of makes an attempt) x 100
You’ll be able to’t calculate error charge in a vacuum. You additionally want to determine your product’s general error prevalence charge (EOR). You try this by dividing the overall variety of errors by the overall variety of doable errors. This gives you a median towards which to match task-specific error charges.
Your UX and product groups use this data to determine errors, prioritize them, and allocate sources.
Churn Price
Churn charge measures what number of customers cease utilizing a product inside a specified time. It’s an essential quantity to know, as a result of it helps you perceive how profitable your product is at preserving customers onboard.
It’s 5-25% more expensive to amass a brand new buyer than retain present ones. Maintaining present prospects completely satisfied and your churn charge low is a strong enterprise resolution.
You want two items of knowledge to calculate churn charge. The variety of customers you had firstly of an outlined interval (week/month/12 months) and the variety of customers you misplaced throughout the identical interval. Divide the variety of misplaced customers by the overall variety of prospects.
Churn Price = (# of misplaced customers / complete variety of customers at begin date) x 100
In the event you had 1,000 customers on the beginning date and misplaced 200 in the course of the outlined time interval, your churn charge can be 20%.
(200 / 1,000) x 100 = 20%
Decrease churn charges imply increased consumer retention.
Churn charge alone doesn’t inform UX groups what there’s to repair. Nevertheless it is step one in diving deeper into the consumer expertise to determine what points there could be. When churn charge is excessive, UX and product groups can look critically at different metrics, like time on job, error charge, and job success charge to develop a plan for design enhancements.
Retention Price
Retention charge measures the share of customers who maintain utilizing a product over a given time period. The upper your retention charge, the higher on your backside line.
The commonest approach companies calculate retention charge within the context of internet sites and apps is to measure customers each month. You divide the lively customers nonetheless round at first of the second month with the variety of lively customers firstly of the primary month.
Retention Price = (# of lively customers in second month / complete # of lively customers firstly of the primary month) x 100
In case you have 1,000 customers on January 1 and 900 of those self same customers are nonetheless with you at first of February, your retention charge is 90%.
You’ll be able to modify this formulation to measure every other interval you want. Cellular groups will usually measure every day retention at days 7, 14, and 30 (D7, D14, and D30). Ecommerce and retail firms will usually measure annual repurchase charges.
Simply be sure to don’t consider new prospects that have been acquired between durations. Take a single cohort of customers or prospects, then measure how that group modified by the second interval.
UX groups can have a major influence on user retention. Frictionless onboarding, streamlined checkout, and different parts of the consumer expertise are all issues the UX group can optimize to spice up retention charges. The group can begin with a baseline, make design modifications, then measure once more to see how these modifications influenced retention charge.
Search vs. Navigation
Understanding how customers get round your web site is measured by evaluating those that use your navigation menu versus those that depend on the search possibility. Each choices are essential to have on any web site, however search requires more cognitive effort from the user. It’s essential to have a well-designed navigation system in place.
You measure each navigation and search with the identical formulation–variety of duties accomplished through search or navigation divided by the overall variety of accomplished duties. To do the comparability, you do the calculation twice, as soon as for navigation and as soon as for search. You then examine the chances.
Proportion of Navigation = (Variety of duties accomplished with navigation / complete variety of accomplished duties) x 100
Proportion of Search = (Variety of duties accomplished with search / complete variety of accomplished duties) x 100
Sometimes, you’ll get about 30 percent of site visitors using your search function. The remaining are relying in your navigation menu.
When the share of search is excessive in comparison with navigation, it might point out that one thing in your navigation system is complicated or damaged. This suggestions off the UX group to re-evaluate how menus are structured and implement options to make issues smoother.
This doesn’t imply that search doesn’t have its relevance. The UX group must additionally deal with that, since search performance is an integral part of fine web site design, especially on mobile devices. Search customers are likely to convert up to 5-6 times higher than non-search customers.
Click on-Via Price
Click on-through charge (CTR) calculates the variety of customers who click on on a design ingredient, like a call to action, versus the overall variety of customers who noticed it throughout a specified timeframe. The CTR measures how profitable your web site or app is at partaking customers and getting them to take a desired motion.
Calculating CTR requires two items of knowledge–the variety of clicks on a component and the overall variety of web site or app guests to the web page the place the ingredient is situated. Right here’s the formulation:
CTR = (Variety of clicks / Variety of views) x 100
For instance, in case your CTA button obtained 100 clicks and was seen by 1,000 customers, your CTR charge can be 10%.
CTR permits UX groups to determine design parts which are underperforming. This helps the group prioritize enchancment on these design parts and allocate sources successfully. CTR can repeatedly be measured after design modifications are made to gauge the effectiveness of the modifications.
Conversion Price
Conversion charge is the share of customers who visited your web site and accomplished a specified job in comparison with the overall variety of web site guests. It’s a measure of how simple it’s for guests to get what they need whereas in your web site or app.
You calculate conversion charge by dividing the variety of conversions by the variety of complete guests.
Conversion charge = (Variety of Conversions / Variety of Web site Guests) x 100
When conversion charges are low, UX groups can use different metrics like time on job and error charges to pinpoint drawback spots in a course of circulation. This helps allocate design sources effectively and resolve them shortly.
Let’s say you need a web site customer to fill out and submit a type, however you’re having bother with low conversion charges for that objective. It might be that the shape itself is the problem. It could possibly be too lengthy or ask for an excessive amount of delicate data within the first few questions.
The UX group can revise the shape design to make it shorter (or break it up into smaller sections) and put the delicate asks in direction of the top. Effectively-designed kinds construct consumer belief and encourage type completion. Customers who’ve labored by way of nearly all of the shape are extra prepared to supply the delicate data they could not have been prepared to surrender at first.
System Usability Scale (SUS)
The System Usability Scale (SUS) is a ten query survey an individual completes after utilizing a product. The solutions are subjective, however can be utilized to calculate an general SUS rating that helps information product selections.
Right here’s an instance of a SUS questionnaire from the Journal of User Experience. Whereas the wording of your questions would possibly differ barely relying on what you’re testing, the format and query order is similar for each SUS questionnaire. That’s by design.
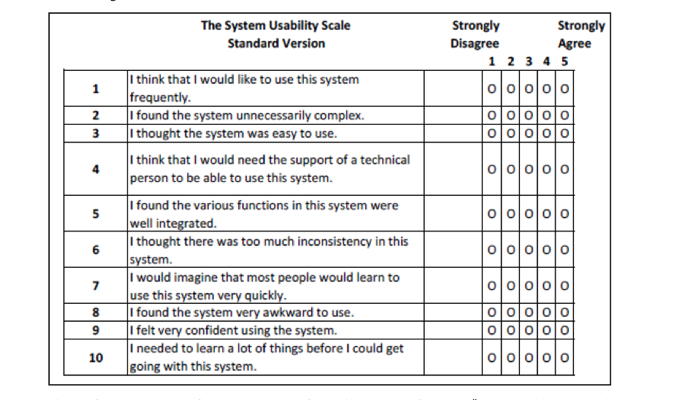
The odd quantity questions ask about constructive issues, and the even quantity questions ask about unfavorable issues. This helps stop a consumer’s tendency to test the identical worth down the web page on these kinds of questionnaires. This format does make the SUS rating a bit advanced, however there are calculators that may assist.
A SUS rating helps UX groups determine wanted design updates and guides them to prioritize their work. Modifications get carried out and new SUS scores will be obtained to gauge the effectiveness of the modifications.
Buyer Satisfaction (CSAT)
The client satisfaction rating measures how glad customers are with a product or characteristic. This UX metric is among the best to implement. You ask customers a single query.
“How glad are you with _______________?”
The consumer charges their satisfaction on a scale of 1 (very unhappy) to five (very glad). You calculate the CSAT by including up all of the respondents that gave a 4 or 5 score, then dividing that by the overall variety of respondents and multiplying that determine by 100. The upper the share, the upper buyer satisfaction.
CSAT = (Variety of 4 & 5 Rankings / Complete variety of responses) x 100
Sometimes, CSAT is concerning the quantity score. However to make the CSAT extra useful for UX groups, you possibly can add a remark part so customers can elaborate on their score. This offers concrete information about particular points that influenced the rating.
UX groups can use the feedback to determine ache factors and formulate options. Then, after design updates are made, assessment new CSAT rating feedback to see the influence of the modifications.
Web Promoter Rating (NPS)
The Web Promoter Rating (NPS) quantifies how possible customers are to advocate a product to buddies, household, or colleagues. NPS is closely tied to the user experience. When customers discover your product simple to make use of, they’re extra prone to advocate it to another person.
NPS is calculated by asking customers a single query.
“How possible are you to advocate __________ to another person?”
The consumer chooses their response on a scale of 0 (unlikely) to 10 (very possible). Responses are grouped into Detractors (0-6), Passives (7-8), and Promoters (9-10). You subtract the share of detractors from the share of promoters to calculate an general NPS. The upper the NPS rating, the extra completely satisfied customers you will have.
NPS = (# of Promoters/complete # of respondents) – (# of Detractors/complete # of respondents)
Let’s say you surveyed 100 individuals, with 60 supplying you with a Promoter rating, 20 supplying you with a Detractor rating, and the opposite 20 giving a Passive rating. Your NPS can be 40.
60% Promoter Rating – 20% Detractor Rating = NPS of 40
It’s also possible to embrace a remark subject in your NPS quiz to permit respondents to additional clarify their score. Whereas this data will not be formally a part of the NPS, it may be a useful useful resource to know the “why” with a view to information product and design modifications.
Advertising groups love NPS, as a result of a excessive quantity lets them inform successful story to stakeholders. However this type of data is useful to UX groups, too, particularly when the remark subject is included. Customers usually add feedback that may level to design or performance flaws, serving to designers and builders resolve these points effectively, enhance the consumer expertise, and increase NPS scores.
Accessibility
Each web site has to supply an equal expertise to each consumer, it doesn’t matter what limitations a consumer has. It’s not only a authorized factor, it’s an moral one. You need your web site or app to be inclusive, not unique.
Accessibility requirements are specified by the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). One huge a part of this for the UX group is designing a web site that’s appropriate with display screen readers. Accessibility is among the most essential web design best practices.
Display screen reader compatibility assessments 5 issues–non-text content material (charts, pictures, illustrations), headings, type labels, keyboard interplay, and on-page hyperlinks. There are lots of free and paid instruments and providers on the market that designers and builders can use. In the event you’re undecided the place to begin, the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) has an inventory of testing instruments they endorse.
The accessibility metrics offered by these instruments tells you ways properly your web site or app accommodates customers with disabilities. UX groups can use these metrics to make modifications to a web site to ship a full, wealthy expertise for each consumer.











