The celebs aren’t mounted and unchanging, not like what many historical individuals thought. On occasion, a star seems the place there wasn’t one earlier than, after which it fades away in a matter of days or even weeks.
The earliest document of such a “visitor star,” named so by historical Chinese language astronomers, is a star that all of the sudden appeared in skies around the globe on July 4, 1054. It shortly brightened, turning into seen even in the course of the day for the subsequent 23 days.
Astronomers in Japan, China, and the Center East noticed this occasion, as did the Anasazi in what’s now New Mexico.
Within the second half of 2024, a nova explosion within the star system T Coronae Borealis, or T CrB, will as soon as once more be seen to individuals on Earth. T CrB will seem 1,500 occasions brighter than normal, however it gained’t be as spectacular because the occasion in 1054.

I’m a space scientist with a ardour for instructing physics and astronomy. I really like photographing the night time sky and astronomical occasions, together with eclipses, meteor showers, and once-in-a-lifetime astronomical occasions such because the T CrB nova. T CrB will grow to be, at greatest, the fiftieth brightest star within the night time sky—brighter than solely half the celebs within the Massive Dipper. It would take some effort to seek out, however when you have the time, you’ll witness a uncommon occasion.
What Is a Nova?
In 1572, the well-known Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe noticed a brand new star within the constellation Cassiopeia. After reporting the occasion in his work “De Nova Stella,” or “On the New Star,” astronomers got here to affiliate the phrase nova with stellar explosions.
Stars, no matter dimension, spend 90 percent of their lives fusing hydrogen into helium of their cores. How a star’s life ends, although, is dependent upon the mass of the star. Very huge stars—these greater than eight occasions the mass of our solar—detonate in dramatic supernova explosions, like those individuals noticed in 1054 and 1572.
In decrease mass stars, together with our solar, as soon as the hydrogen within the core is exhausted, the star expands into what astronomers name a crimson large. The crimson large is lots of of occasions its authentic dimension and extra unstable. Ultimately, all that’s left is a white dwarf—an Earth-sized remnant made up of carbon and oxygen. White dwarves are 100 thousand occasions denser than diamond. Until they’re a part of a binary star system, the place two stars orbit one another, they slowly fade in brightness over billions of years and finally disappear from sight.
T CrB is a binary star system—it’s made up of a red giant and a white dwarf, which orbit one another each 228 days at about half the gap between Earth and the solar. The crimson large is nearing the tip of its life, so it has expanded dramatically, and it’s feeding materials right into a rotating disk of matter known as an accretion disk, which surrounds the white dwarf.
Matter from the accretion disk, which is made largely of hydrogen, spirals in and slowly accumulates on the floor of the white dwarf. Over time, this blanket of hydrogen turns into thicker and denser, till its temperature exceeds 18 million levels Fahrenheit (10 million levels Celsius).
A nova is a runaway thermonuclear reaction just like the detonation of a hydrogen bomb. As soon as the accretion disk will get scorching sufficient, a nova happens the place the hydrogen ignites, will get blown outward, and emits vibrant mild.
When Will It Happen?
Astronomers know of 10 recurrent novae—stars which have undergone nova explosions greater than as soon as. T CrB is probably the most well-known of those. It erupts on common each 80 years.
As a result of T CrB is 2,630 light-years from Earth, it takes mild 2,630 years to journey the gap from T CrB to Earth. The nova we’ll see later this 12 months occurred over 2,000 years in the past, however its mild will probably be simply reaching us.
The accretion of hydrogen on the floor of the white dwarf is like sand in an 80-year hourglass. Every time a nova happens and the hydrogen ignites, the white dwarf itself is unaffected, however the floor of the white dwarf is cleaned of hydrogen. Quickly after, hydrogen begins accreting on the floor of the white dwarf once more: The hourglass flips, and the 80-year countdown to the subsequent nova begins anew.
Cautious observations throughout its previous two novae in 1866 and 1946 confirmed that T CrB turned barely brighter about 10 years earlier than the nova was seen from Earth. Then, it briefly dimmed. Though scientists aren’t positive what causes these brightness adjustments, this sample has repeated, with a brightening in 2015 and a dimming in March 2023.
Primarily based on these observations, scientists predict the nova will probably be seen to us someday in 2024.
How Shiny Will It Be?
Astronomers use a magnitude system first devised by Hipparchus of Nicaea greater than 2,100 years in the past to categorise the brightness of stars. On this system, a distinction of 5 in magnitude signifies a change by an element of 100 in brightness. The smaller the magnitude, the brighter the star.
In darkish skies, the human eye can see stars as dim as magnitude 6. Ordinarily, the seen mild we obtain from T CrB comes completely from its crimson large, a magnitude 10 star barely seen with binoculars.
Throughout the nova occasion, the white dwarf’s exploding hydrogen envelope will brighten to a magnitude 2 or 3. It would briefly grow to be the brightest star in its dwelling constellation, Corona Borealis. This most brightness will final solely a number of hours, and T CrB will fade from visibility with the bare eye in a matter of days.
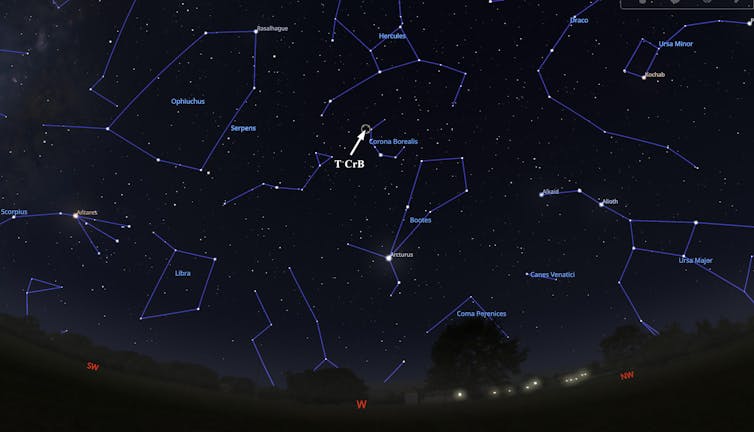
The place to Look
Corona Borealis shouldn’t be a outstanding constellation. It’s nestled above Bootes and to the west of Ursa Major, dwelling to the Massive Dipper, in northern skies.
To find the constellation, look due west and discover Arcturus, the brightest star in that area of the sky. Then look about midway between the horizon and zenith—the purpose straight above you—at 10 p.m. native time in North America.
Corona Borealis is roughly 20 levels above Arcturus. That’s in regards to the span of 1 hand, from the tip of the thumb to the tip of the pinky, at arm’s size. At its brightest, T CrB will probably be brighter than all the celebs in Corona Borealis, however not as vibrant as Arcturus.
You can too use an interactive star chart reminiscent of Stellarium, or one of many many apps accessible for smartphones, to find the constellation. Familiarizing your self with the celebs on this area of the sky earlier than the nova happens will assist establish the brand new star as soon as T CrB brightens.
Though T CrB is just too removed from Earth for this occasion to rival the supernova of 1054, it’s nonetheless a possibility to look at a uncommon astronomical occasion with your individual eyes. For many people, this will probably be a once-in-a-lifetime occasion.
For youngsters, nevertheless, this occasion may ignite a ardour in astronomy. Eighty years sooner or later, they could stay up for observing it as soon as once more.
This text is republished from The Conversation below a Artistic Commons license. Learn the original article.
Picture Credit score: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center











