SaaS metrics present solutions to essential questions: how can we enhance buyer acquisition? How worthwhile are our clients? What do we have to do earlier than we pitch our next funding round?
However the bother is, many corporations monitor the flawed SaaS metrics, within the flawed approach, or worse nonetheless, overlook essential metrics solely. As an alternative of utilizing metrics as a helpful assist to efficiency, they find yourself complicated the image.
That will help you perceive and enhance your efficiency, I’ve put collectively a complete information to 50 important SaaS metrics (loosely divided into Development, Advertising, Gross sales and Buyer Success).
For every of the 50 metrics, we’ll take a look at:
- What they’re, and why they matter.
- calculate them to your personal SaaS firm.
- Benchmarks to information your efficiency.
- Recommendation from founders and investors.
This useful resource was final up to date in December, 2024.
SaaS Development Metrics
Startups are so arduous that you may’t be pointed off to the facet and hope to succeed. It’s a must to know that progress is what you are after. The excellent news is, in the event you get progress, every part else tends to fall into place. Which implies you should utilize progress like a compass to make nearly each resolution you face.
SaaS progress metrics are designed to analyse the “momentum” of your enterprise as a complete: your capacity to develop, and continue to grow.
Consider them just like the heartbeat, blood stress and temperature of your organization: the core indicators that reveal the well being of your subscription enterprise at its most elementary stage.
By combining collectively parts of gross sales, advertising and buyer success, these metrics present a transparent indication of your total efficiency, in a handful of key figures (it is for that purpose they typically type a vital a part of any investor’s due diligence).
Attending to grips with these SaaS metrics will show you how to to:
- Perceive how your enterprise is growing, and the place efficiency may be improved.
- Create a dashboard of at-a-glance SaaS metrics to remain on high of your organization’s well being and efficiency.
- Talk the worth of your rising enterprise to would-be buyers.
1) Month-to-month Recurring Income (MRR)
SaaS companies are subscription-based, and the recurring nature of this cost mannequin makes it comparatively simple to trace and forecast income, in a approach that different enterprise fashions battle to do. That is the place MRR is available in: we will work out the quantity of predictable income generated by our clients every month, often known as Monthly Recurring Revenue.
MRR is important for understanding the expansion of your enterprise, and with a very good deal with on buyer acquisition and churn charges (which I am going to cowl beneath), we will even use it to extrapolate to the long run, and predict future income.
$$textual content{MRR}_t=sumtext{Recurring Income}_t$$
The essential components for MRR is fairly easy: for any given month (interval t), merely sum up the recurring income generated by that month’s clients to reach at your MRR determine.
Within the following instance, in January we have now 2 clients, every paying a month-to-month subscription of $2,000. In February, we achieve an extra buyer, and MRR will increase because of this. In March, we achieve an extra buyer:
$$textual content{January: }2000+2000=4000 textual content{ MRR}$$
$$textual content{February: }2000+2000+2000=6000 textual content{ MRR}$$
$$textual content{March: }2000+2000+2000+2000=8000 textual content{ MRR}$$
The one metric that I search for is the essential MRR…
Each SaaS firm ought to reside and die by MRR, as a result of that’s one thing that you may’t go with out.
2) Annualized Run Charge (ARR)
ARR stands for Annualized Run Charge (I’ve additionally seen it known as Annual Recurring Income). In easy phrases, it is the recurring income generated by your SaaS enterprise over the course of a 12 months:
$$textual content{ARR}=textual content{MRR}times12$$
Most SaaS companies generate the vast majority of their income from month-to-month subscriptions, making MRR the clearest indicator of income era. Nonetheless some companies deal primarily in yearly contracts, making ARR a better and clearer metric to make use of.
…most enterprise SaaS corporations ought to use annual recurring income (ARR), not month-to-month recurring income (MRR), as a result of most enterprise corporations are doing annual, not month-to-month, contracts…
3) Buyer Churn
As a subscription-based enterprise, your progress relies on new buyer acquisition, and crucially, minimising the lack of your current clients. Buyer churn (sometimes called “Brand Churn”) measures the speed at which your current clients cancel their subscription to your service.
$$textual content{Buyer Churn Charge}=frac{textual content{Clients that churned in interval t}}{textual content{Whole clients in the beginning of interval t}}$$
For instance, if we begin January with 20 paying clients, however end the month with solely 19, the client churn fee for January alone was 5%:
$$textual content{Buyer Churn Charge}=frac{20-19}{20}=5%$$
Annual buyer churn charges
It is essential to trace each month-to-month and annual buyer churn charges, for one quite simple purpose: affordable sounding month-to-month churn can shortly flip into crippling annual churn.
For instance, I’ve seen a number of estimates for a target annual churn of 5-7% – utilizing the components beneath, that interprets to roughly 0.5% month-to-month churn, or a lack of 1 buyer in each 200.
$$textual content{Annual Buyer Churn Charge}=(1-(1-text{Month-to-month Churn Charge}))^{12}$$
$$6percentapprox(1-(1-0.005))^{12}$$
In distinction, a comparatively innocent sounding 5% month-to-month churn fee interprets into a large 54% churn fee over the course of the 12 months:
$$textual content{Annual Buyer Churn Charge}=(1-(1-0.05))^{12}approx54%$$
That is helpful for extrapolating annual churn from a single month-to-month churn determine, however in case you have 12-months of knowledge, you should utilize that to calculate the 12 months’s actual buyer churn determine:
$$textual content{ACCR }=1-(1-m_1)instances(1-m_2)instances…instances(1-m_{11})instances(1-m_{12})$$
Clients That Cannot Churn
These which can be in any other case certain by a contract couldn’t churn this month, so if we determine them into our churn calculation, we’d seem like we’re doing higher than we truly are.
Every month, there’s more likely to be a portion of your buyer base that’s currently unable to churn: sometimes as a result of they’re nonetheless certain by their contract (as an instance you provide a month-to-month rolling contract with a 3-month minimal committment).
Factoring these individuals into your churn statistic will truly under-report your real churn rate, so it is a good suggestion to exclude these individuals out of your calculations:
$$textual content{Buyer Churn Charge}=frac{textual content{Churned clients}_t}{textual content{Beginning clients}_t-text{Certain clients}_t}$$
Churn Cohorts
Equally, measuring churn is not a aim in its personal proper: we wish to perceive the why behind churn, and repair it. By grouping collectively clients with comparable attributes (resembling month joined, or the size of time they have been a buyer), we can create churn cohorts to try to establish the triggers that trigger excessive churn.
Cohort analyses are the solely technique to get a very good understanding of retention and buyer lifetimes.
4) Income Churn
Income churn (additionally known as “MRR churn fee”) is used to have a look at the speed at which month-to-month recurring income (MRR) is misplaced, because of misplaced clients and downgraded subscriptions.
$$textual content{Income Churn Charge}=frac{textual content{MRR}_{t-1}-text{MRR}_t}{textual content{MRR}_{t-1}}$$
For instance, if we generate $5,000 MRR throughout January, however because of our earlier misplaced buyer, solely $4,750 throughout February, that month’s income churn is $250, or 5%:
$$textual content{Income Churn Charge}=frac{5,000-4,750}{5,000}=5%$$
Damaging income churn
The examples above are fairly easy: 5% buyer churn resulted in 5% income churn. In actuality although, completely different pricing packages, and extra seats, customers and storage, could make churn calculations much more complicated.
For instance, think about we have been capable of upsell 4 of our present clients to a better priced bundle, for an extra $250/month.
Although our buyer churn fee stays the identical, the month’s income churn is definitely adverse: regardless of shedding a buyer, our upselling has lead to higher revenue than the earlier month:
$$textual content{Buyer Churn Charge}=frac{20-19}{20}=5%$$
$$textual content{Income Churn Charge}=frac{5,000-5,750}{5,000}=-15%$$
5) Bookings
Bookings information the whole worth of all new offers obtained over a time interval. Crucially (and in contrast to MRR), Bookings figures make no distinction between up-front and recurring funds.
$$textual content{Bookings}_t=sumtext{Worth of New Offers}_t$$
For instance, if a buyer bought a 12 months’s subscription for $24,000, that month’s bookings determine could be $24,000, however the month’s MRR could be $2,000 ($24,000 / 12).
As a common rule, monitoring Bookings is a helpful approach of measuring cashflow, however MRR is extra useful for measuring income progress over time.
The way in which we’ve measured “Income” has been to take the whole income we generated within the month, and use that. For “Annual income run fee,” we merely multiplied month-to-month income by 12.
Our income consists of individuals who pay us on a month-to-month foundation and likewise those that pay for the entire 12 months upfront. That is the place the miscalculation lies.
As a recurring income (SaaS) enterprise, we will’t assure we’ll get the identical variety of individuals paying for annual subscriptions month after month, and we’re counting income that’s sooner or later. The proper approach is to ‘amortize’ and divide these annual funds by 12.
On this approach, we’re solely counting the following 12 months of precise recurring income we have now already acquired.
6) MRR Development Charge
The MRR Development Charge is extraordinarily helpful for measuring the development of your income era over time.
$$textual content{MRR Development Charge}=frac{textual content{MRR}_t-text{MRR }_{t-1}}{textual content{MRR }_{t-1}}times100$$
For instance, if we generated $1,500 MRR final month, and elevated that to $2,000 this month, we might have an MRR Development Charge of roughly 33%:
$$textual content{MRR Development Charge}=frac{2000-1500}{1500}times100approx33%$$
A gradual month-on-month MRR Development Charge is indicative of fast, exponential progress, because it requires extra income every month to maintain the identical progress fee.
MRR Development Charge is among the the highest metrics SaaS corporations ought to monitor as a result of it solutions the query ‘How briskly is the corporate rising?’
7) Internet New MRR
MRR Development Charge is beneficial, however it may be deceptive. True exponential progress is extraordinarily uncommon, and within the early days of a SaaS startup (when your income era is low in absolute phrases), reporting on this determine can conflate true exponential progress with step enhancements to your income: in spite of everything, it is simple to double your MRR for a number of months when your place to begin is $100.
For many SaaS companies, it is extra helpful to report on the quantity of recent income generated every month, versus the share progress fee that income represents. That is performed by breaking down your MRR figures, and grouping collectively MRR from completely different sources:
- New MRR is income gained from new subscriptions.
- Enlargement MRR is income gained because of successful upselling and cross-selling.
- Churned MRR is income misplaced because of clients cancelling their subscription.
- Contraction MRR is income misplaced because of clients downgrading their subscription.
- Reactivation MRR is income generated by a beforehand churned buyer returning to a paid subscription.
Utilizing this data, we will then calculate Internet New MRR: the extra MRR generated, after we have taken into consideration MRR misplaced to churn.
$$textual content{Internet New MRR }=textual content{New MRR + Enlargement MRR – Churn MRR}$$
For instance, if we generated $10,000 in new MRR, and an extra $1,000 in upselling income, however misplaced $2,000 because of churn, we might have a Internet New MRR determine of $9,000:
$$textual content{Internet New MRR }=10000+1000-2000=9000$$
…so long as you’re at a really low absolute ranges (say beneath ~ $20k in MRR in the event you’re a SaaS startup) it doesn’t make an excessive amount of sense to speak about proportion progress charges, and speaking about progress when it comes to internet new MRR per thirty days could also be extra helpful.
8) SaaS Fast Ratio
The SaaS Fast Ratio is designed to check your income progress over a selected time interval (as proven by New MRR + Enlargement MRR) along with your income shrinkage over the identical timeframe (as proven by Churned MRR + Contraction MRR).
$$largetext{SaaS Fast Ratio}=frac{(textual content{New MRR}_t+textual content{Enlargement MRR}_t)}{(textual content{Churned MRR}_t+textual content{Contraction MRR}_t)}$$
Devised by Social Capital founder Mamoon Hamid, it creates a easy ratio of progress to churn, and offers a transparent indicator of the well being of your income progress, and never simply its pace.
For instance, think about your income is rising by $1,000 per thirty days. We’d assume that progress would break down as follows:
$$+1000text{ New MRR, }-0text{ Churned MRR}$$
However there are all-manner of different ways in which progress might be occurring:
$$+2000text{ New MRR, }-1000text{ Churned MRR}$$
$$+5000text{ New MRR, }-4000text{ Churned MRR}$$
Although the general progress fee is identical, the underlying well being of those companies may be very, very completely different. The final firm is having to generate $4,000 of recent income, every month, simply to maintain its head above water.
Should you’re on the lookout for one thing to intention for, evaluation of real-world SaaS Fast Ratios confirmed that profitable, quick rising SaaS corporations maintain an average Quick Ratio of 3.9.
I used to be all the time taking a look at this one metric, Month-to-month Recurring Income – how a lot month-to-month income you get out of your SaaS clients. Nonetheless, I wished to know extra…
…If the corporate has a Fast Ratio of 4, they’re rising at a wholesome fee, and have a low sufficient churn fee for me to take a position.
9) Burn Charge
Burn Charge refers back to the fee at which corporations use their money provide over time.
There are two forms of Burn Charge metrics generally utilized in SaaS:
- The Gross Burn Charge refers back to the sum of money an organization spends in a month.
- The Internet Burn Charge refers back to the quantity the corporate loses in a month (Gross Burn Charge – Income). If earned income is bigger than the quantity spent in a month, Internet Burn will likely be adverse.
Burn Charge is especially essential to buyers as a result of it offers a sign of when a startup ought to look to boost its next round of startup funding. For instance, with a Internet Burn Charge of $200,000, and $2 million within the financial institution, the corporate has 10-months of money remaining (sometimes called the corporate’s “money runway”). If that burn fee elevated to $400,000, the runway could be lowered to 5-months.
Some SaaS founders additionally select to make the excellence between Base Burn Charge and Development Burn Charge:
Base Burn is the sum of money the corporate spends to function: actual property, salaries, advantages, authorized charges – the entire working prices of the enterprise.
Development Burn consists of the advertising and gross sales prices of recent buyer acquisition.
Founders managing their enterprise this manner intention to drive the enterprise to profitability on Base Burn. Going through a money scarcity, the startup may reduce all new buyer acquisition to generate revenue.
10) Zero Money Date
Zero Money Date (ZCD) is the expected date your startup runs out of money, because of your present burn fee, and assuming no new income era.
Your ZCD offers a sign of when new funding should be sought, and as your startup turns into cashflow constructive and builds up its money reserves, your ZCD ought to transfer additional and additional into the long run.
11) Value of Items Offered (COGS)
COGS refers back to the Value of Items Offered: the entire expenditure related to serving clients and delivering your answer. For a software-as-a-service enterprise, the most typical COGS embrace:
- Utility internet hosting charges.
- Third-party internet charges (like CDNs or licensing for merchandise embedded within the utility).
- Buyer help prices.
12) Gross Margin
Figuring out your COGS is a crucial a part of calculating your Gross Margin: the share of your income left over after the price of servicing that income (i.e. the prices of delivering the service that generated the income) is taken into consideration.
$$textual content{Gross Margin %}=frac{textual content{Income}-text{COGS}}{textual content{Income}}$$
For instance, if an organization generated $50,000 of income over a selected interval, and needed to spend $7,000 on internet hosting and $3,000 on buyer help over that very same interval, their Gross Margin on that income could be 80%, or $40,000.
$$textual content{Gross Margin %}=frac{50000-(7000+3000)}{50000}=80%$$
Excessive gross margins are an indicator of software-as-a-service companies, and the upper your gross margin, the extra income you could have accessible to take a position again into progress.
If the corporate is an ecommerce enterprise with 20% gross margins (commodity merchandise) vs a SaaS enterprise with 80% gross margins, each further greenback of income for the SaaS enterprise is equal to 4 {dollars} within the ecommerce enterprise (because of the a lot larger contribution margin).
Margin is among the important causes a $10 million income firm may be extra helpful than a $100 million income firm.
SaaS Advertising Metrics
…the way in which I’ve all the time checked out it’s that advertising is admittedly the gasoline to the hearth. When you’ve obtained nice product/market match, advertising and all of the completely different instruments that we have now, every part from promoting to nurturing to conversion fee advertising to separate testing to positioning messaging, these are all of the instruments that may assist simply speed up that progress additional.
Fast, large-scale buyer acquisition is a pre-requisite for progress, and these marketing-specific SaaS metrics are designed that can assist you perceive and enhance your capacity to generate new guests, leads and clients.
In addition to offering perception into buyer acquisition, these SaaS metrics will assist decide the standard of your leads. In any case, SaaS marketing and gross sales should not exist in seperate silos, and web site guests and leads do not imply a factor except they flip into paying clients.
With each features having a vital (and overlapping) function to play in attaining progress, it is essential to decide on metrics that cowl each camps.
Understanding Funnel Metrics
As an example you could have a aim of 100 new clients this 12 months. As a way to attain these 100 clients, you would possibly want 200 engaged, ready-to-buy leads: in spite of everything, not all people you begin a dialog with finally ends up a paying buyer.
Working backwards, to generate these 200 sales-qualified leads, you would possibly want to gather the contact particulars of 400 individuals, a few of whom could have a critical curiosity in your merchandise, whereas others would require a bit extra time to succeed in the identical place. To generate these 400 leads, you would possibly want 2,000 web site guests.
Understanding how this development by means of the gross sales funnel occurs means that you can predict the variety of guests and leads you may must truly hit your gross sales targets, and provides course to your advertising technique.
You’ll want to measure the variety of prospects going into every stage, and the conversion fee to the following stage. Additionally, you will care concerning the total conversion fee of prospects from the highest of funnel to closed deal, and the common deal measurement.
The form of your funnel will possible differ for every completely different lead supply, e.g. leads from Fb advertisements could not convert nicely into trials, however people who do convert to trials could have a better conversion fee to closed offers than regular internet visitors, and the deal sizes could also be bigger. Meaning you’ll need to trace the funnel metrics individually by lead supply.
These metrics will present you your funnel blockage factors, and show you how to perceive whether or not your actions to enhance funnel stream are working.
13) Distinctive Web site Guests
Distinctive web site guests refers back to the variety of distinct folks that go to your web site over a selected time frame (generally a month).
Guests are available all sizes and shapes, from sales-ready patrons to sceptical researchers (and even just a few individuals who’ve ended up in your website by mistake). As a way to decide which guests are which, and establish potential clients, it is important to be taught extra about them.
14) E-mail Subscribers
E-mail subscribers are guests who’ve signed up to your publication, mailing record or weblog updates. Although they’ve parted with their contact particulars, they have not proven any indication of gross sales intent, or curiosity in your SaaS product, making them distinct from leads.
15) Leads
Leads are primarily guests who’ve willingly transitioned from passive observers to energetic contributors in your advertising funnel. By filling out a contact type—typically in alternate for a helpful useful resource resembling an e-book, a white paper, or a free trial—they show a sure stage of curiosity in what it’s a must to provide. As an alternative of merely looking your content material and transferring on, these people have taken a step ahead, indicating that they’re probably extra certified prospects than the common web site customer.
In offering their contact data, leads transcend simply surrendering their electronic mail handle. They often share further private {and professional} particulars like their identify, job title, and even their firm’s web site or enterprise identify. This wealth of knowledge provides you a chance to realize insights into their skilled context, tailor your communications, and create a extra personalised expertise. In the end, leads signify a useful asset: they aren’t merely web page views or click-throughs, however actual individuals who have proven real curiosity in constructing a relationship along with your model.
16) Advertising Certified Leads (MQLS)
MQLs, or Advertising Certified Leads, are prospects who haven’t solely demonstrated the best demographic and firmographic traits of a possible buyer however have additionally proven real curiosity in your services or products. This curiosity typically manifests itself by means of tangible actions in your web site or advertising channels. For instance, they might spend time looking product-specific sections, resembling case research that showcase your answer in motion, or pricing pages that element the associated fee and worth of what you provide. Moreover, these leads would possibly have interaction with varied product-focused content material gives, resembling downloadable guides, comparability charts, or trial sign-ups, additional signaling that they’re evaluating your enterprise as a viable possibility.
This heightened stage of engagement, mixed with acceptable demographic alignment, elevates MQLs past the standing of informal guests and leads. By scrutinizing which pages they view and what content material they eat, you’ll be able to infer their place within the purchaser’s journey and gauge their stage of readiness to progress within the gross sales funnel. Geared up with these insights, your advertising and gross sales groups can implement extra personalised and efficient outreach, making certain that MQLs are guided in the direction of a dialog with gross sales representatives at simply the best second. In the end, MQLs signify a crucial stepping stone within the pipeline, standing at a juncture the place advertising’s affect begins to intersect with direct gross sales engagement.
17) Gross sales Certified Leads (SQLS)
SQLs, or Gross sales Certified Leads, are those that haven’t solely met the preliminary advertising qualification standards however have taken clear steps in the direction of a possible buy. These leads stand out as a result of they’ve moved past merely exploring your content material and choices; they’ve actively signaled a readiness to interact along with your gross sales group. As an example, a lead could request a one-on-one session, join a product demo, or instantly inquire about pricing and implementation. Such actions present concrete proof that the prospect is inquisitive about studying extra about how your answer can handle their particular challenges.
This shift in engagement from informal exploration to express outreach represents a pivotal second within the gross sales course of. By this level, an SQL has sometimes gathered sufficient details about your product, has evaluated its relevance to their issues, and is now keen to interact in additional in-depth discussions. In consequence, these leads warrant speedy consideration out of your gross sales group, who can now give attention to understanding the potential buyer’s distinctive wants and guiding them towards a tailor-made answer. In the end, SQLs carry a better chance of conversion, making them indispensable property in transferring your pipeline towards profitable, revenue-generating outcomes.
18) Alternatives
Alternatives signify a crucial turning level within the lead-to-customer journey. As soon as a Gross sales Certified Lead has been handed over to the gross sales group, the group rigorously evaluates their wants, timing, funds, and decision-making capabilities. By way of conversations, assessments, and preliminary rapport-building, the gross sales group determines whether or not the prospect is a real potential purchaser who’s price pursuing additional. When a lead clears this vetting course of and is confirmed as a high-value candidate for conversion, they formally turn into a possibility. At this stage, the lead is not only a identify within the database, however somewhat a viable deal that may be actively pursued.
This transition into a possibility marks the start of a extra structured and intentional gross sales course of. The gross sales group can now delve deeper into understanding the prospect’s distinctive challenges, show how their software program can meet these challenges, and description potential options tailor-made to the client’s particular wants. From right here, each side have interaction in additional substantive discussions, negotiations, and answer positioning. By labeling a lead as a possibility, the group commits further time and assets in the direction of successful this account, understanding that the trouble is justified by the chance of a profitable and mutually helpful partnership.
19) Paying Clients
These are folks that have signed on the dotted line and comitted to paying to your service for a selected size of time. Although extra of a gross sales metric, it is essential to trace how marketing-generated leads convert into paying clients, as a way to assess the general efficiency of your advertising technique.
20) Free Trials & Demo Requests
Many SaaS merchandise use free trials and demos to interact potential clients, and it is essential to grasp the place these match into the gross sales funnel.
Free Trial customers are normally counted as MQLs: signing-up for something “free” requires comparatively little committment from customers, and easily kicking the tyres of your product offers no indication of gross sales intent.
Some SaaS merchandise may be extra advanced, and require customized set-up earlier than use. This typically signifies that free trials aren’t viable, and as a substitute, operating product demos is a more practical approach of proving out the worth of your product.
Getting on the telephone and sitting by means of a demo requires a better committment out of your guests, so demo requests are normally considered SQLs. Although the excellence is not all the time clear, it is essential to decide on a easy, constant rule for qualification, and keep on with it.
If advertising drove these leads and obtained them to the purpose the place they’re “certified” … it ought to be designated a Advertising Certified Lead (MQL).
If somebody from the gross sales group manually did the qualification … whatever the lead supply, name it a Gross sales Certified Lead (SQL).
Understanding Conversion Charges
There are two methods to generate extra clients: growing the variety of individuals getting into the gross sales funnel, and bettering the speed at which guests flip into leads, and leads flip into clients.
Although lead and buyer acquisition ought to all the time be a precedence, it is typically doable to generate extra leads and clients, at a decrease value, by bettering your conversion charges. Step one in bettering conversion charges is to trace them at essential factors of your gross sales funnel.
21) Customer to Lead
The speed at which web site guests convert into leads. Instruments like pop-ups, electronic mail subscriptions, free downloads and landing pages can all be used to transform nameless guests into identifiable leads, and it is essential to optimise this conversion fee over time.
$$textual content{Customer to Lead conversion fee}=frac{textual content{Variety of Leads}}{textual content{Variety of Guests}}$$
22) Result in Buyer
That is an overarching conversion fee that appears on the fee at which leads convert into clients. Producing a lot of poor-fit leads will result in a particularly low conversion fee, and vice versa, so this will provide a really revealing perception into the standard of the leads you are producing.
$$textual content{Result in Buyer conversion fee}=frac{textual content{Variety of Clients}}{textual content{Variety of Leads}}$$
23) MQL to SQL
This exhibits the speed at which marketing-qualified leads flip into sales-qualified leads, and it may possibly present helpful insights into lead high quality and the efficiency of your gross sales growth reps.
$$textual content{MQL to SQL conversion fee}=frac{textual content{Variety of SQLs}}{textual content{Variety of MQLs}}$$
24) Free Trial to Paid Buyer
That is the speed at which free trial customers turn into paying clients. Small enhancements to this determine will generate massive enhancements in income, so it is essential to repeatedly optimise your free trial onboarding process.
$$textual content{Free Trial to Buyer conversion fee}=frac{textual content{Variety of Clients}}{textual content{Variety of Free Trials}}$$
For a B2B SaaS firm with free trial, I assume the next ball park figures:
– 3%-5% – common and means good enterprise operations
– 8% and above – glorious conversion charges
– beneath 3% – beneath common
25) Advertising Spend:Common Contract Worth
The ratio of your advertising spend to Common Contract Worth (which I am going to go into beneath) is beneficial for monitoring how expenditure on advertising channels interprets into gross sales income.
$$textual content{Advertising Spend:Annual Contract Worth}$$
26) Month-on-Month MQL Development Charge
Month-on-Month MQL Development Charge refers back to the fee at which Advertising Certified Leads are rising over time.
$$textual content{MoM MQL Development Charge}=frac{textual content{MQLs}_t-text{MQLs }_{t-1}}{textual content{MQLs }_{t-1}}times100$$
For instance, if we generated 100 advertising certified leads final month, and 110 this month, we might have month-on-month MQL progress of 10%.
$$textual content{MoM MQL Development Charge}=frac{110-100}{100}times100=10%$$
27) Month-on-Month SQL Development Charge
In addition to monitoring the MQL progress fee, we will additionally monitor the speed of progress of sales-qualified leads (SQLs):
$$textual content{MoM SQL Development Charge}=frac{textual content{SQLs}_t-text{SQLs }_{t-1}}{textual content{SQLs }_{t-1}}times100$$
For instance, if we generated 50 gross sales certified leads final month, and 60 this month, we might have month-on-month SQL progress of 20%.
$$textual content{MoM SQL Development Charge}=frac{60-50}{50}times100=20%$$
SaaS Gross sales Metrics
One of many myths of SaaS is that the merchandise are so good, really easy to make use of, so fast to deploy … that the product sells itself. Given the recognition of try-before-you-buy and freemium-to-premium fashions for software program as a service, it’s simple to see the place that delusion comes from.
However as many startups uncover to their horror — after they “land” customers and attempt to “increase” to extra departments in a big firm or authorities company — that is removed from the reality. Even with early viral progress, SaaS merchandise don’t promote themselves.
Regardless of how “sticky” or “viral” your app turns into, the continued progress of your SaaS enterprise will rely upon efficient gross sales processes.
The SaaS metrics collected right here will show you how to decide every part from the effectivity of your gross sales group by means of to the validity of your pricing mannequin. Crucially, they’re going to additionally provide you with a lot wanted perception into your clients, when it comes to their anticipated lifetime, profitability and worth.
In any case, there’s extra to scaling a SaaS enterprise than buying clients: you should purchase the best forms of buyer.
28) Annual Contract Worth (ACV)
Annual Contract Worth appears on the worth of a buyer’s contract over a 12-month interval.
For instance, if a buyer dedicated to a 24-month contract of $60,000, that contract would generate $2,500 in MRR ($60,000/24 months) and $30,000 in ACV ($60,000/2 years).
29) Whole Contract Worth (TCV)
TCV stands for Whole Contract Worth, and appears on the worth of a buyer’s contract over its whole length.
Returning to the instance above, our buyer’s 24-month contract of $60,000 has a TCV of $60,000. If, on the finish of their contract, that very same buyer bought a special product, paying $10,000 for a 6-month interval, the TCV of that contract could be $10,000.
In contrast to measurements of recurring income, each TCV and ACV measure all income generated throughout the chosen timeframe: together with one-off funds and fees.
30) Common Income per Account (ARPA)
ARPA stands for Common Income Per Account, and is used to measure how a lot income is contributed by an “common” account or buyer, per thirty days. Modifications to ARPA may be useful for monitoring progress and income era on a per unit foundation.
$$textual content{ARPA}=frac{textual content{MRR}}{textual content{Variety of energetic accounts}}$$
It is useful to trace ARPA seperately for each new clients and current clients. This makes it simple to check the traits and income era of your clients over time: seeing how they reply to upselling and cross-selling over their lifetime.
31) Common Promoting Worth (ASP)
ASP stands for Common Promoting Worth (or Common Sale Worth). The place ARPA appears on the common quantity of income a buyer contributes throughout the course of a month, ASP measures the common preliminary value that clients pay on the time of gross sales conversion:
$$textual content{ASP}=frac{sumtext{Deal Income}}{textual content{Variety of offers}}$$
Understanding your ASP is the important thing to figuring out the best gross sales mannequin to your SaaS startup – self-service, transactional or enterprise – as your ASP locations a restrict on the Buyer Acquisition Value you’ll be able to justify (extra on that beneath). A excessive ASP makes high-touch gross sales methods viable, and a low ASP forces you in the direction of a self-service mannequin.
I don’t know any single statistic that gives extra perception on a SaaS startup, or any enterprise for that matter, than common promoting value (ASP).
32) Buyer Acquisition Value (CAC)
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is designed to inform you how a lot you should spend to amass a single new buyer.
For many B2B SaaS companies, the prices of buying a brand new buyer are decided by two elements:
- The prices of producing a lead (normally decided by advertising bills).
- The prices of changing that lead right into a buyer (usually a results of gross sales prices, or contact prices – the salaries of gross sales growth reps or discipline gross sales individuals).
Sometimes, the best technique to work out the price of securing a single new buyer is to bundle collectively the whole gross sales and advertising expenditure in a given time interval (interval t), and divide it by the whole variety of new clients.
$$textual content{CAC}_t=frac{textual content{Gross sales and Advertising Value}_t}{textual content{New Clients}_t}$$
For instance, in the event you spent $5,000 apiece on gross sales and advertising in a given month, and closed 10 new clients over that very same time interval, that month’s Buyer Acquisition Value could be $1,000:
$$frac{5000+5000}{10}=1000$$
CAC and Buyer Success
Most CAC calculations deliberately exclude the prices and income related to customer success strategies.
Though buyer success groups generate (typically important) income, by means of upselling, cross-selling and inspiring renewals, CAC is designed to measure your capacity to generate new income from gross sales and advertising expenditure.
Including buyer success into the calculation distorts that measurement, so it is best to trace individually.
Free vs Paid Clients
Should you generate leads from each paid and unpaid channels, it is essential to calculate acquisition cost separately for each.
With 100 “free” clients (generated with a $0 CAC) and 20 clients at $500 CAC, the common CAC is roughly $83. This “blended” CAC is correct, however when it comes to understanding your gross sales and advertising methods, fairly ineffective.
Dave Kellog’s Various CAC
As an alternative of producing an summary greenback worth, Dave Kellogg recommends an alternate CAC calculation that compares your gross sales and advertising expenditure within the earlier interval (S&Mt-1) to the brand new income generated within the present interval (New ARRt).
This successfully tells you ways a lot you are spending to generate a single greenback of recent buyer income:
$$textual content{CAC}_t=frac{textual content{Gross sales and Advertising Value}_{t-1}}{textual content{New ARR}_t}$$
For instance, in the event you spent a mixed whole of $10,000 on gross sales and advertising final month, and generated $12,000 in new income this month, that signifies that for each $1 of recent income, you needed to spend $0.83 to realize it.
$$frac{5000+5000}{12000}=0.83$$
Some individuals say, for instance, {that a} CAC of two.0 [paying $2 CAC for $1 ARR] is dangerous. Properly, in the event you’re promoting a month-to-month product the place most clients discontinue by month 9, then a CAC of two.0 is horrific.
Nonetheless, in the event you’re promoting sticky enterprise infrastructure, changing programs which were in place for a decade with purposes that may nicely be in place for one more decade, then a CAC is 2.0 might be high-quality.
That’s the purpose: there isn’t any absolute proper or flawed reply to what an organization ought to be prepared to pay for a buyer. What you might be prepared to pay for a buyer ought to be a operate of what they’re price.
33) CAC Payback Interval
Clients will solely turn into worthwhile once they’ve generated sufficient income to cowl their acquisition value, and it may be extraordinarily useful to work out how lengthy this “payback interval” will likely be.
The components for the CAC Payback Interval (additionally known as Months to Get well CAC) is simple: simply divide the price of buying a buyer by the month-to-month income they generate, to work out what number of months’ income it requires to break-even.
$$textual content{CAC Payback Interval}=frac{textual content{CAC}}{textual content{MRR per buyer}}$$
For instance, with a buyer acquisition value of $2,000, and a median month-to-month income per buyer of $150, it’s going to take simply over a 12 months for every buyer to turn into worthwhile:
$$textual content{CAC Payback Interval}=frac{2000}{150}approx13text{months}$$
34) Gross Margin Adjusted Payback Interval
Though your MRR goes in the direction of paying again your acquisition value, it is also contributing to the additional prices related to offering your service (COGS, #11).
By factoring the Gross Margin into our components, we will calculate a extra correct payback interval:
$$textual content{Gross Margin Adjusted Payback Interval}=frac{textual content{CAC}}{(textual content{MRR per buyer}timestext{Gross Margin})}$$
Utilizing the CAC Payback Interval instance from earlier, and a gross margin of 70%, we now generate a CAC payback interval of 19 months: 6 months longer than beforehand estimated, because of the COGS your MRR must cowl.
$$textual content{CAC Payback Interval}=frac{2000}{150}approx13text{months}$$
$$textual content{Gross Margin Adjusted Payback Interval}=frac{2000}{150times0.7}approx19text{ months}$$
Goal to get well your CAC in < 12 months, in any other case your enterprise would require an excessive amount of capital to develop.
35) Buyer Lifetime Worth (LTV)
LTV (typically known as CLTV or CLV) stands for Buyer Lifetime Worth: the whole quantity of income generated by a single buyer over the lifetime of their subscription to your SaaS product.
LTV exhibits you ways a lot every buyer is contributing to your income, and for the way lengthy, and guides how a lot you need to be spending to amass them (extra on that within the subsequent metric). By segmenting LTV by completely different buyer sorts and buyer personas, you may as well hone in in your most beneficial clients.
$$textual content{LTV}=frac{textual content{ARPA}}{textual content{Buyer churn fee}}$$
For instance, with an Common Income Per Account of $200, and a ten% Buyer Churn Charge, we might generate a Lifetime Worth of $2,000:
$$textual content{LTV}=frac{200}{0.1}=2000$$
36) LTV:CAC
Neither CAC nor LTV imply a lot in isolation: you’ll be able to solely work out how “good” your CAC is in relation to the income these clients generate (LTV).
$$textual content{LTV:CAC}$$
For instance, in case your buyer’s lifetime worth was $2,000, and it value $1,000 to amass that buyer, that is an LTV:CAC ratio of two:1.
$$$2,000:$1,000$$
$$2:1$$
It is sensible that your LTV ought to all the time be better than your CAC: few companies wish to lose cash on each buyer they purchase.
Past this, previous efficiency means that LTV needs to be about 3x CAC for a SaaS enterprise to outlive. Greatest-in-class performers (like Salesforce and Fixed Contact) do even higher, with multiples nearer to 5x.
An essential word right here is that your LTV may be decrease than your CAC in sure situations, however all of these hinge on you ultimately making up the deficit by means of new merchandise, options, income sharing, and many others.
Moreover, some enterprise backed corporations forgo LTV for very excessive CAC to run a “scorched earth” technique of buying logos. That is dangerous, however an efficient technique in the event you’re in a “winner take all” kind market.
37) Win Charge
Your Win Charge is used to offer a easy take a look at gross sales effectivity, and the power of your gross sales reps to shut offers. It appears on the variety of offers received, as a proportion of whole offers (these received and misplaced). It can be calculated utilizing the greenback worth of these offers:
$$textual content{% Win Charge}=frac{textual content{Received Alternatives}}{textual content{Received Alternatives}+textual content{Misplaced Alternatives}}$$
Clearly, a excessive win fee is indicative of an efficient gross sales group and a excessive lead high quality. However within the early days of your SaaS startup, a excessive win fee is not all the time one thing to intention for. As an alternative, it is possible an indication that you just’re coasting alongside, counting on simple offers as a substitute of pushing into new segments and markets.
Whenever you first begin, it’ll seem to be you win nearly each deal — since you aren’t in very many.
Then as you scale, you truly need your total win fee to go down (whereas sustaining your lead in your core segments of first traction).
After which return up when you’re a lot, a lot larger and win the larger prize.
38) Gross sales Fee:ACV
In the case of scaling your gross sales group, there is a easy mathematical constraint in operation: gross sales individuals must promote greater than they value.
As an alternative of monitoring the price of your gross sales group in isolation, you’ll be able to as a substitute measure gross sales fee as a proportion of Annual Contract Worth (ACV), and instantly relate gross sales prices to the income they’re concerned in producing.
$$textual content{Gross sales Fee:ACV}=frac{textual content{Gross sales Fee}}{textual content{Annual Contract Worth}}$$
For instance, with a gross sales fee of $500, and an Annual Contract Worth of $5,000, gross sales fee could be 10% of ACV (or 10:1 – roughly the median gross sales fee:ACV ratio in SaaS).
$$textual content{Gross sales Fee:ACV}=frac{500}{5,000}times100= 10%$$
I’ve labored with salespeople, who come from giant organizations, typically demand fee charges within the 20%-25% vary.
Unbeknownst to startups, these charges aren’t “market” within the SaaS world. Actually, that median gross sales fee is roughly 9% of Annual Contract Worth (ACV) for the previous two years.
39) Gross sales Effectivity
Gross sales effectivity is usually referred because the “Magic Quantity” of SaaS, as a result of it gives a transparent, easy technique to perceive the return generated by your progress (when it comes to gross sales and advertising) investments.
$$textual content{Gross sales Effectivity}=frac{textual content{Income}timestext{Gross Margin %}}{textual content{Gross sales and Advertising Prices}}$$
For instance, if a SaaS firm generates $1.25 million in income with an 80% Gross Margin, and spends a complete $500,000 on gross sales and advertising, they’d have a gross sales effectivity of two.
$$textual content{Gross sales Effectivity}=frac{1250000times 80%}{250000 +250000}= frac{1000000}{500000}= 2$$
Gross sales Effectivity is the inverse of the payback interval: the size of time it takes for patrons to “pay again” the prices of buying them. For a very good benchmark to intention for, a magic variety of 1 signifies that gross sales and advertising expenditure will likely be recouped by buyer income within the subsequent 4 quarters.
Most SaaS corporations function across the 0.8 mark, which means the enterprise pays again the price of the income and gross sales expense within the 5 quarters of the client.
40) Income per Lead
Income Per Lead permits you’re employed out the common quantity of income every lead (versus buyer) will contribute. By calculating Income per Lead on a per-sales-person foundation (utilizing solely their energetic leads as a pattern), it offers an awesome perception into the effectivity of your whole gross sales group (and the forms of leads they’re tasked with closing).
$$textual content{Income Per Lead}=frac{textual content{ACV}}{textual content{Variety of leads}}$$
I would advocate calculating Income per Lead utilizing cohort analysis: wanting on the ACV income generated by a selected “batch” of leads (say leads generated in January), versus dividing ACV (a product of closed offers and thus “outdated” leads) by your present leads.
Leads are treasured for a very long time in startups, and if you may get 20 % extra out of every lead, that’s magic.
However in the event you don’t measure it right down to the person rep stage and also you simply take a look at MRR, you’re lacking a possibility to enhance issues.
41) Lead Velocity Charge
Most of the metrics we use to evaluate (and predict) our progress are literally caught previously.
In the identical approach that mild from distant stars exhibits us an image from tens of millions of years in the past, most gross sales and income metrics replicate offers that have been created months and years previous.
In different phrases, in the event you’re attempting to make use of present gross sales offers to foretell future gross sales, you are utilizing outdated data, and obsessing over alternatives created by your outdated gross sales and advertising methods, not your present strategy.
Lead Velocity Charge (often known as Lead Momentum or Certified Lead Development) is a fast and easy approach of measuring the month-on-month progress of your lead era:
$$textual content{LVR}=frac{textual content{Certified Leads}_{t}-text{Certified Leads}_{t-1}}{textual content{Certified Leads}_{t-1}}times100$$
For instance, if we generated 100 certified leads final month (t-1), and 110 this month (t), we might have a lead velocity fee of 10%:
$$textual content{LVR}=frac{110-100}{100}times100=10%$$
What fee are your certified leads rising month over month?
Your MRR progress is nice, however actually that simply tells you concerning the current – the way you’re doing now. But when your leads are rising quicker than your income, I can see the long run progress.
Having the ability to quantifiably monitor the rate of certified leads goes to be your absolute best indicator as a CEO of the place you’re going to be sooner or later.
SaaS Buyer Success Metrics
…“buyer success” is a type of imprecise phrases that looks like it was invented once we wanted a buzzword to explain what profitable companies have been doing endlessly.
However simply because it’s a buzzword doesn’t imply that it’s not completely crucial to give attention to. It’s.
Nearly each profitable software program firm that I can consider has gotten to the place they’re – or not less than to preliminary traction – on the success of their clients.
Buyer acquisition can really feel just like the be-all and end-all for growth-hungry startups, however the larger you get, the more durable it turns into to take care of the identical fast progress charges.
Buyer acquisition alone is not sufficient to maintain your progress, and if you begin to achieve traction, it is important to your precedence to shift. Instead of continuous to fixate in your gross sales and advertising methods, it is time to give attention to Customer Success: fuelling progress by means of the retention and upselling of your current clients.
These SaaS metrics are designed to grasp buyer behaviour – how (and why) they’re participating with your enterprise – permitting you to enhance the worth your enterprise delivers to its clients, and develop your income because of this.
42) Every day Energetic Customers (DAU)
DAU stands for Every day Energetic Customers, and it is a easy measurement of the variety of energetic customers on a given day (interval d):
$$textual content{Every day Energetic Customers}=textual content{Variety of Energetic Customers}_d$$
The important thing to making a useful DAU or MAU metric is to carefully define how users qualify as “active”. Many SaaS corporations use DAU to depend the variety of customers who logged in on a selected day, with out differentiating between a person that logs in to make use of each side of their product’s performance, and one other that logs in to ship help requests and delete their knowledge.
Whereas this may be useful for easy reporting functions, it does nearly nothing to disclose how engaged customers truly are along with your product, or predict retention charges and at-risk clients.
As an alternative, it is higher to create a extra discerning definition of “energetic”. Although this may scale back the scale of your DAU or MAU measurement, it creates a way more helpful metric.
43) Month-to-month Energetic Customers (MAU)
MAU is the month-to-month counterpart to DAU, and stands for Month-to-month Energetic Customers: a measure of the whole variety of “energetic” customers in a given month (interval m).
$$textual content{Month-to-month Energetic Customers}=textual content{Variety of Energetic Customers}_m$$
When you usually must sign-in to an app to get worth, that motion alone might be not the factor that delivers worth to your buyer.
Merely being “energetic” within the product doesn’t imply you’re being “profitable” both.
Actually, quite a lot of logins and random in-app exercise might be an indication that your buyer can’t work out what to do… however they certain want to.
It’s a sign that one thing’s amiss… however quite a lot of corporations would possibly wrongly classify that buyer as “energetic” and subsequently “onboard” and “profitable.”
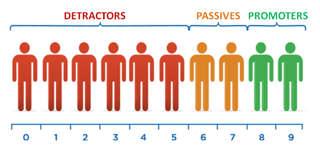
44) Internet Promoter Rating (NPS)
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a software that is used to try to quantify buyer satisfaction along with your service. The NPS makes use of a easy survey query:
“How possible are you to advocate
[your SaaS product] to a good friend or a colleague?”
Respondents are then requested to decide on a corresponding rating, on a scale from 0 (“In no way possible”) to 10 (“Extraordinarily possible“).
Your Internet Promoter Rating is then calculated by subtracting the share of Detractors from the share of Promoters. A constructive rating suggests extra individuals prepared to advocate your product than these attempting to dissuade others from utilizing it – you are receiving a internet promotion – and vice versa.
$$textual content{NPS}=%textual content{Promoters}-%textual content{Detractors}$$
For instance, if 50% of responders have been promoters, and 10% of respondents have been detractors, your NPS could be 40:
$$textual content{NPS}=50%-10%=40$$
In line with Zendesk, the median NPS score for B2B companies is 29.
Like most SaaS corporations, we use drip NPS — just a few of our clients reply to an in-app NPS survey each day.
This provides us a continuing pulse of suggestions. The entire group will get to high-five once we get one other “10.” And, if there’s ever a buyer situation, the product group is fast to supply help.
When everyone seems to be aligned round buyer happiness, the CSM’s job is way simpler.
45) Buyer Satisfaction Rating (CSAT)
In contrast to the Internet Promoter Rating, Buyer Satisfaction (or CSAT) scores are used to fee particular person interactions along with your firm. After an interplay (say a buyer help dialog or closing an upselling deal), the client is requested a easy query:
“How would you fee your total satisfaction with the service you obtained?”
Respondents then rating their interplay from 1 (very dissatisfied) to five (very glad). CSAT scores are then calculated by averaging out these responses:
$$textual content{CSAT}=frac{sum textual content{Buyer Responses}}{5timestext{Variety of Responses}}times100$$
For instance, if we surveyed 5 clients about their experiences, and 4 responded with a 5, and one with a 3, we might have a CSAT rating of 92% (with 100% reflecting full satisfaction):
$$textual content{CSAT}=frac{5+5+5+5+3}{5times5}times100=92%$$
As your SaaS enterprise grows, monitoring your buyer interactions turns into each more durable, and extra essential to do. CSATs can present a easy window into the kind of service you provide, and features as a helpful complement to NPS measurements.
46) Upsell & Cross-sell Charge
The Upsell Charge means that you can calculate the share of a interval’s income that was generated from upselling: encouraging current clients to extend their spend, by buying extra seats, extra space for storing, going to a higher-priced tier, and many others.
$$textual content{Upsell Charge}=frac{textual content{ACV of Upsells}_t}{textual content{Whole ACV}_t}$$
For instance, if we generated $10,000 in Annualised Contract Worth over a single month, and $2,500 of that income can from upselling, the upsell fee could be 25%:
$$textual content{Upsell Charge}=frac{2500}{10000}times100=25%$$
The identical calculation may be utilized to cross-selling, to work out the proportional income generated by encouraging clients to take-up complementary providers (like buying an invoicing product to work alongside their recurring billing software):
$$textual content{Cross-sell Charge}=frac{textual content{ACV of Cross-sells}_t}{textual content{Whole ACV}_t}$$
Doing proper by our clients is precedence numero uno, so we don’t try and upsell except it is sensible for our buyer’s enterprise.
47) Viral Coefficient
Buyer referrals is usually a highly effective contributor to progress, and the viral coefficient is a approach of measuring the growth of your customer base generated by profitable buyer referrals.
Merely put, your Viral Coefficient tells you what number of new customers a present person is referring to your enterprise. Understanding and bettering the viral coefficient of your SaaS answer is an important a part of attaining explosive, ‘viral’ progress.
$$frac{(textual content{Variety of Customers} instances textual content{Common Variety of Referrals} instances textual content{Referral Conversion Charge})}{textual content{Variety of Customers}}$$
The instance beneath assumes 100 customers, every sending out 10 buyer referrals. These referrals convert into new paying clients at a fee of 15%, producing a Viral Coefficient of 1.5:
$$textual content{Viral Coefficient }=frac{(100times 10times 0.15)}{100}=frac{150}{100}=1.5$$
A Viral Coefficient better than one signifies that for each new person you purchase, you may achieve an extra person (or extra) because of profitable referrals. On this instance, a coefficient of 1.5 means every new buyer is, in flip, producing 1.5 further clients because of the referral course of.
True exponential progress may be very, very uncommon in SaaS…
…even a modest exponential progress fee of 10% p.m. may be very arduous to maintain for an extended time frame.
Any such really viral progress (the place progress is self-sustaining by means of referrals alone) is fairly unobtainable, however a viral coefficient of lower than one continues to be massively helpful.
Receipt monitoring service Shoeboxed calculated that that they had a viral coefficient of 0.2. Although not really “viral”, this nonetheless culminates in a single further referred buyer for each 5 new clients, successfully growing progress by 20%:
$$frac{(100times 4times 0.05)}{100}=frac{20}{100}=0.2$$
I’d say sometimes, SaaS apps don’t have sufficient clients to see the fabric, financial advantages of viral income till they cross $1m-$2m in ARR on the earliest. You may even see hints of it earlier than, and in your leads, however normally, there aren’t sufficient clients or time for it to maneuver the needle as a fabric income contributor earlier than then.
Now, in the event you’re constructing a free B2C app, the place you want tens of tens of millions of customers to get to Preliminary Scale, that’s a catastrophe.
However in SaaS, if you’re on a 7-10 12 months journey to $100m in ARR, it truly doesn’t matter that a lot in case your viral coefficient is low if you get the viral clients. Sooner is best after all. But it surely’s all nonetheless good, as long as it comes and it’s not the one supply of recent clients. And when it does come, it comes on materially, and powerful.
48) Referral Income
Referral Income is an easy combination measurement of all of the income generated by profitable buyer referrals, over a selected time interval. Buyer referrals are a cheap channel of progress, and it is essential to intention for a rise in Referral Income over time.
With that stated, Referral Income figures alone solely present you easy tendencies in income; and to unlock extra helpful insights, it is essential to check Referral Income to the funding in Buyer Referral that generated it.
49) Referral Return on Funding (ROI)
If we wish to go a step additional than calculating Referral Income, we will use Referral Return on Funding (ROI) to check the quantity we’re spending on buyer referrals with the income these referrals will generate over their lifetime.
Think about our common buyer pays $1,000/month, for a lifetime of two years:
$$textual content{LTV }=1000times24=24000$$
For our referral scheme, we’re providing an incentive of 20% off the month-to-month invoice ($1,000 x 0.2 = $200), for 12 months, to each profitable referrals and profitable referrers:
$$textual content{Value of Referral Incentive }=(200times12)+(200times12)=4800$$
We are able to use that data to work out the Referral ROI: a quantity that exhibits what number of {dollars} in LTV we’re producing for every greenback of referral advertising spend:
$$textual content{Referral ROI}=frac{textual content{LTV}-text{Referral Incentive}}{textual content{Referral Incentive}}$$
Given our instance above, we’re producing $4.5 in LTV for each $1 we’re spending on the referral:
$$textual content{Referral ROI}=frac{24000-4800}{4800}=4.5$$
50) Viral Referral ROI
Importantly although, Buyer Referral packages truly enhance your LTV: along with the direct income clients will generate over their lifetime, they now have a hand in producing income from different clients, because of profitable referrals.
As a way to enhance our Referral ROI, it is a good suggestion to issue this into the equation. The components beneath is modified in a single regard: the LTV is now modulated by our Viral Coefficient, or the common fee at which current clients generate new clients, because of referrals.
$$textual content{Viral Referral ROI}=frac{textual content{(LTV}instances(1+textual content{Viral Coefficient}))-text{Referral Incentive}}{textual content{Referral Incentive}}$$
If we generate a brand new buyer from the referral efforts of each 5 current clients, we might have a viral coefficient of 0.2. This truly will increase the ROI of our buyer referral program, from 4.5 to five:
$$textual content{Viral Referral ROI}=frac{(24,000times(1+0.2))-4,800}{4,800}=5$$
A Closing Thought on SaaS Metrics
Many corporations fail to trace greater than a handful of SaaS metrics. Others build-out large dashboards of KPIs however pay little greater than lip-service to its findings. To my thoughts, that is simply as dangerous.
It is essential to transcend the shiny dashboard of graphs and inexperienced arrows, and use your SaaS metrics to positively influence your progress. It does not matter that you just’re seeing month-on-month progress of web site guests if none of them flip into leads. Should you’ve doubled your buyer acquisition however trebled your churn, you continue to have an enormous downside.
Metrics alone will not repair something: they’re solely a software to assist you make knowledgeable (and sometimes troublesome) selections. However armed with the perception they supply, you can also make a alternative with as a lot knowledge as doable. Whether or not you are optimising your pricing technique, lowering buyer churn or boosting your free trial-to-customer conversion fee, these SaaS metrics will assist illuminate the best path to take.
Advisable Studying
- SaaS Metrics 2.0, ForEntrepreneurs
- Customer Acquisition: Maximizing your Funnel, ForEntrepreneurs
- Metrics that Make a Difference, Joel York
- SaaS Metrics – Definitions, Joel York
- 5 Key Sales and Marketing Metrics to Track for SaaS, Openview Partners
- Four Important Data Points On Measuring Your Startup’s Customer Happiness, Tomasz Tunguz
- 16 Startup Metrics, Andreessen Horowitz
- 9 Worst Practices in SaaS Metrics, Christoph Janz
- Key Revenue Metrics for SaaS Companies, Christoph Janz
- Metrics, Dave Kellog
- 50+ Benchmarks for Software Startups, Cobloom